Types of Inflammation – Inflammation is a part of the body’s defense mechanism and thus plays a significant role in healing. When the body notices an intruder, it launches a biological response to eliminate the problem.
The invader might be an external body, such as a tingling, an irritant, or a pathogen. Pathogens include bacteria, viruses, and also other organisms , that cause infection. Sometimes, the body wrongly notices its cells or tissues as harmful. This reaction results in autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes.
Experts say that inflammation may contribute to a varied range of chronic diseases. Some of these are metabolic syndrome, which consists of type 2 diabetes, heart illness, and also obesity. Therefore people with these conditions frequently have higher irritation signs in their bodies. Please learn more about the reason for the inflammation, its symptoms, and also the ways to resolve it.
Types and Symptoms of Inflammation
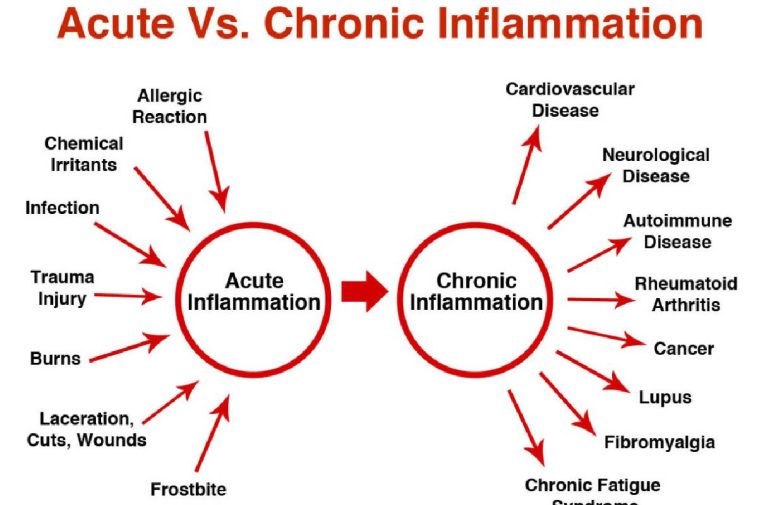
There are two basic types of trusted sources of inflammation: acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation
A wound or infection can involve severe or temporary inflammation.
There are five critical signs of acute inflammation:
- Pain may happen endlessly or only when a person touches the affected part.
- Redness: This occurs due to a rise in the blood supply to the capillaries in that part.
- Loss of function: There may be trouble moving a joint, breathing, detecting smell, etc.
- Swelling: A condition called oedema can grow if liquids shape around.
- Heat: Increased blood flow may result in warming the infected area.
However, these symptoms may not be present all the time. Sometimes inflammation is without any signs. People can also feel exhausted, usually sick and may have a fever.
Signs of acute inflammation proceeds for a few days. Subacute inflammation lasts 14-42 days, according to reliable sources. Chronic inflammation can stay for months or years. It either has or may have relations to different illnesses, such as:
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
- Diabetes
- Arthritis and other joint diseases
- Allergies
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
The symptoms will depend on the disease, including pain and weakness.
Types of Inflammation – Measurement of inflammation

When inflammation is there in the body, there will be a maximum level of reliable sources of substances known as biomarkers. An instance of a biomarker is C-reactive protein (CRP). If a doctor needs to examine inflammation, they may assess CRP levels.
CRP levels increase primarily in older people and then with those who suffers from cancer and obesity. Even diet and exercise may make a change.
Types of Inflammation – Causes
Inflammation occurs when a physical factor triggers an immune reaction. A rash does not certainly mean an infection, but a disease is a reason for it.
Acute inflammation
Acute inflammation may be due to
- Coming in contact with a bee bite or dirt
- An injury
- A contamination
When the body notices damage or pathogens, the immune system triggers several responses:
- Tissues collect plasma proteins, leading to a buildup of fluid that results in puffiness.
- The body issues neutrophils, a white blood cell or leukocyte, that move near the affected part. Leukocytes consist of molecules that can benefit fight pathogens.
- Small blood vessels enlarge trusted sources to allow WBCs and plasma proteins to reach the injury site more easily.
Symptoms of acute inflammation can be seen in a few hours or days, liable on the reason. In some cases, they can quickly become unbearable. Therefore how they grow and how long they stay depends on the cause, which part of the body they affect, and different aspects.
Some factors and infections that can result in severe inflammation are:
- Acute bronchitis, appendicitis and other diseases ending in “-itis.”
- A sore throat through a cold or flu
- Physical shock or wound
- An ingrown toenail
Chronic inflammation
Chronic inflammation can develop if a person has the following:
Sensitivity: Inflammation occurs when the body feels something that should not be there. Supersensitivity to an exterior induction can result in an allergy.
Exposure: Sometimes, long-term, sub-ordinate exposure to an annoyance, such as a manufacturing chemical, can result in chronic inflammation.
Autoimmune illness: The immune system mistakenly attacks normal healthy tissue, as in psoriasis.
Autoinflammatory diseases: A hereditary industry reliable source that affects how the immune system works, such as in Behçet’s disease.
Determined severe inflammation: In some cases, a person may not fully improve from severe inflammation. Sometimes, this can also lead to chronic inflammation.
Factors that may intensify the risk of chronic inflammation include reliable Sources:
- Elder age
- Overweghtness
- A diet that is high in harmful fats and high sugar
- smoking
- Low sex hormones
- stress
- sleep problems
Long-term diseases that doctors associate with inflammation are:
- rheumatoid arthritis
- tuberculosis
- chronic peptic ulcer
- asthma
- periodontitis
- ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease
- sinusitis
- energetic hepatitis
Types of Inflammation – Conclusion
It plays an integral part in curing, but chronic inflammation may raise the danger of several diseases, such as some types of cancers, rheumatoid stiffness, atherosclerosis, and periodontitis.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings